Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized
by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. In epilepsy disorder, brain activity becomes
abnormal.
Seizures are the main symptoms of epilepsy. Seizures are due to brief disturbances in the electrical functions of the brain.
Epileptic seizures are episodes that can range from brief and almost undesirable periods to prolonged vigorous tremors. These episodes can lead to sensations, periods of unusual behavior, and sometimes loss of awareness and physical injuries such as broken bones.
Seizures are the main symptoms of epilepsy. Seizures are due to brief disturbances in the electrical functions of the brain.
Epileptic seizures are episodes that can range from brief and almost undesirable periods to prolonged vigorous tremors. These episodes can lead to sensations, periods of unusual behavior, and sometimes loss of awareness and physical injuries such as broken bones.
 |
| Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder. Seizures are the main symptoms of epilepsy disorder. |
Epilepsy:
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments - How to Prevent Epileptic Seizures
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that causes recurrent,
unprovoked seizures.
Epilepsy is defined as a chronic disease that affects the brain and is caused by two or more unexplained
seizures that cause a direct surge of electricity in the brain.
Seizures can be
defined as hyper-synchronous disorders of nerve signals emitted by the nerves
of the brain, causing disorders in the affected area.
This, in turn, causes
disruption to all functions controlled by the affected area, such as behavior,
sensation, movement, language, standing position, awareness, and perception, and
much more.
It should be noted that
there are different types of seizures and convulsions, but they share the fact
that they are short-lived, often lasts from a few seconds to a few
minutes. Usually, the brain returns to normal functions after a seizure.
Some people may suffer
from problems such as confusion or fatigue and general fatigue after the end of
the seizure for a limited period. However, these symptoms often disappear
after a while and the body returns to normal.
It is worth noting that
episodes of seizures do not necessarily mean epilepsy, but suffering from
epilepsy means an increased risk of seizures in the future.
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Seizures are the main
symptoms of epilepsy. Epilepsy is caused by irregular brain cell activity,
so epileptic seizures can cause damage to any work done by the body and
coordinated by the brain.
An epileptic seizure may
cause temporary confusion, complete loss of consciousness, staring in space or
involuntary shivering movements of the hands and legs.
In most cases, if a person has frequent epileptic seizures, he tends to develop the same signs and
symptoms in each seizure, so that the signs associated with an epileptic seizure
become identical from one seizure to another.
However, other patients
suffer from different types of seizures, whose signs and symptoms vary from
time to time.
In fact, epileptic
seizures and associated symptoms vary according to their type.
Types of Epilepsy
1. Partial
Seizures:
Partial seizures, also known as focal seizures, they are represented by two main types:
Partial seizures, also known as focal seizures, they are represented by two main types:
I. Simple partial seizure: This type of epilepsy is not accompanied by loss of consciousness. Symptoms for simple partial epilepsy include dizziness, tingling in the extremities, and a change in taste, smell, sight, hearing, and touch.
II. Complex partial seizures: These seizures cause loss of consciousness, loss of
responsiveness, and repetition of certain movements.
2. Generalized seizures:
Generalized seizures include the entire brain and have six types that we sum up as follows:
I. Absence seizures: These epileptic seizures cause a slight absence of consciousness and the patient suffers from the repetition of some movements, such as blinking eyes.
II. Tonic
seizures: These epileptic seizures cause muscle stiffness.
III. Atonic
seizures: Atonic seizures cause loss of muscle control, which
increases the chance of a person suddenly falling.
IV. Clonic
seizures: Clonic seizures are characterized by repetitive strange
movements in the muscles of the face, neck, and arms.
V. Myoclonic
seizures: Myoclonic seizures are characterized by strange,
spontaneous, rapid movements in the arms and legs.
VI. Tonic-clonic
seizures: Tonic-clonic seizures are symptoms of unconsciousness,
biting of the tongue, stiffness of the body, and loss of bladder control and
excretion.
Causes of Epilepsy
In fact, there is no specific cause of epilepsy, but it should be noted that the nature of the
symptoms and signs that appear on the injured during a seizure depends on the
affected part of the brain and the speed and extent of transmission of seizures
in the brain.
In fact, there are some
people with genetic factors that play a role in the onset of the disease. Other
factors that increase the chance of epilepsy include:
⇨Some brain health
problems, such as tumors and stroke, are a major cause of epilepsy in people
over 35 years of age.
⇨The brain is hit, for
example during accidents.
⇨Suffering from dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
⇨Lack of oxygen supply to
the brain.
⇨Infectious diseases such
as AIDS, viral encephalitis, and meningitis.
⇨Injury or brain damage
before birth.
⇨Suffering from severe
illness or fever.
⇨Age: People under the age of 20 and those over 65
are more likely to have epilepsy.
Common Epilepsy Seizure Triggers
There are several
factors that trigger the onset of epileptic seizures, including:
⇒Lack of sleep and autism.
⇒Exposure to fever or
disease.
⇒Exposure to tension, or
bright lights.
⇒Take alcohol, caffeine,
and some types of medications.
⇒Skip some meals,
overeating, or eating certain types of foods.
First Aid for Epilepsy Patients
It is advised to follow
some things to help people with seizures, especially tonic-clonic seizures
accompanied by shivering movements. These tips include:
➧Control
the nerves and try to calm down.
➧Remove
all things or objects that may be harmful around the victim, and avoid touching
or approaching the victim.
➧Talk
to the patient calmly and carefully to keep him away from any danger
surrounding him.
➧Support
the head of the victim with a soft pillow if it falls to the ground.
➧Do
not put anything in the mouth of the injured.
➧Monitor
the time, and if the seizure does not end within five minutes, you should call
emergency and seek medical assistance.
➧Ensure
breathing is safe, and the mouth is free from any suspended substances that
cause lightning such as food, tooth, etc.. If the patient has a strange or disturbing voice, seek medical help.
➧Provide
support for the injured and stay with him for a period of time after the end of
the seizure.
How to treat Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
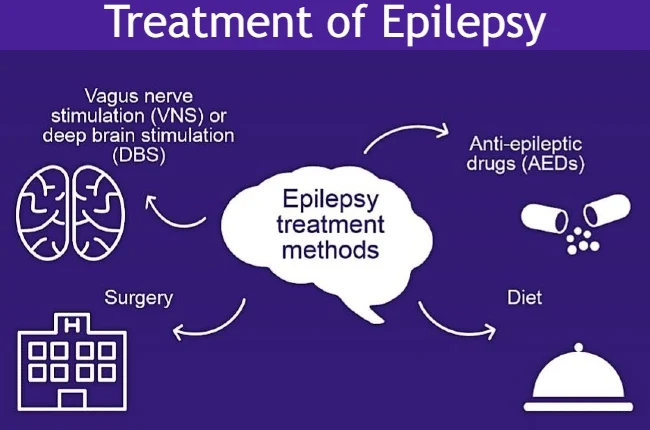 |
| Epilepsy is usually treated by medications such as anticonvulsants and in some cases, it is treated by surgery, devices or dietary changes. |
Treatment of Epilepsy
Treatment is carried out
using a range of medications and drugs that act as anti-epileptic seizures.
If the patient has more
than one type of epilepsy, he is given several types of medications with
specific amounts and times.
If the person has
recurrent and persistent epileptic seizures, the doctor recommends here brain
surgery.
The epilepsy treatment
plan depends on the severity of the symptoms, the health of the victim, and the
extent of the patient's response to the treatment.
Some of the treatment
options available for epilepsy can be described as follows:
Anti-epileptic drugs: Anti-epileptic drugs reduce the number of seizures that occur to the patient and may eliminate them completely in some cases. These drugs depend on the type of epilepsy, the age of the patient, and other factors. The following are common drugs used in the treatment of epilepsy:
- Carbamazepine
- Valproic acid
- Ethosuximide
- Topiramate
It should be noted that
these medicines should be taken exactly as prescribed by the doctor.
Vagus nerve stimulator: Vagus nerve stimulator can place a device (this device resembles a pacemaker) under the skin in the chest area to stimulate the nerve that passes through the neck, reducing the incidence of seizures.
Brain surgery: The area responsible for epileptic seizures in
the brain is removed or replaced.
When medications fail to
control seizures, however, some patients may need to continue taking certain
medications, but at lower doses, as the surgeon during epilepsy surgery,
removes the brain area that causes seizures.
Doctors do this when the
area of the brain where the surgery will be performed does not cause any effect
on other vital functions such as vision and hearing, and also if convulsions
occur in a small area that can be identified in the brain.
Follow the ketogenic
diet: Many people who do
not respond to drug therapy, have been found to benefit from this high-fat,
low-carb diet.
How to Prevent Epileptic Seizures
There are some
guidelines that can reduce and prevent the chance of epilepsy, including:
Prevent traumatic brain
injury: Traumatic brain
injuries are common causes of epilepsy and can be prevented by the following
safety guidelines, wearing a seat belt, wearing a helmet, and other
instructions, especially when driving.
Reduce the chances of
stroke and heart disease: Stroke and heart disease can be reduced by
proper diet, exercise, and smoking cessation. These healthy habits can also
reduce the chance of epilepsy in the future.
Have a vaccination: Some infections contribute to an increased
risk of epilepsy, so have an appropriate vaccination to reduce infectious
disease.
Wash your hands and
prepare food properly: Cysticercosis is
one of the leading causes of epilepsy and can be prevented by the following hygiene
and food preparation guidelines.
Maintain health during
pregnancy: There are many
health problems during pregnancy and childbirth that can lead to epilepsy.
Maintaining health is necessary during this period.
Epileptic seizures can
also be minimized by the following tips:
➮Abstain
from alcohol and drugs.
➮Relax
and control tension and depression.
➮Make
sure you get enough sleep every day.
➮Commit
to taking prescribed medications for epilepsy regularly.
➮Minimize
sitting times in front of your TV or computer screen as much as possible.
➮Avoid
strong lighting and visual stimuli.
➮Avoid
video games.
➮Take
vitamin D and exercise to maintain bone strength and prevent fractures.
Tags
clinical psychology
Epilepsy
epileptic seizures
health
health care
neurological disorders
neuropsychology
Neuroscience
psychology
